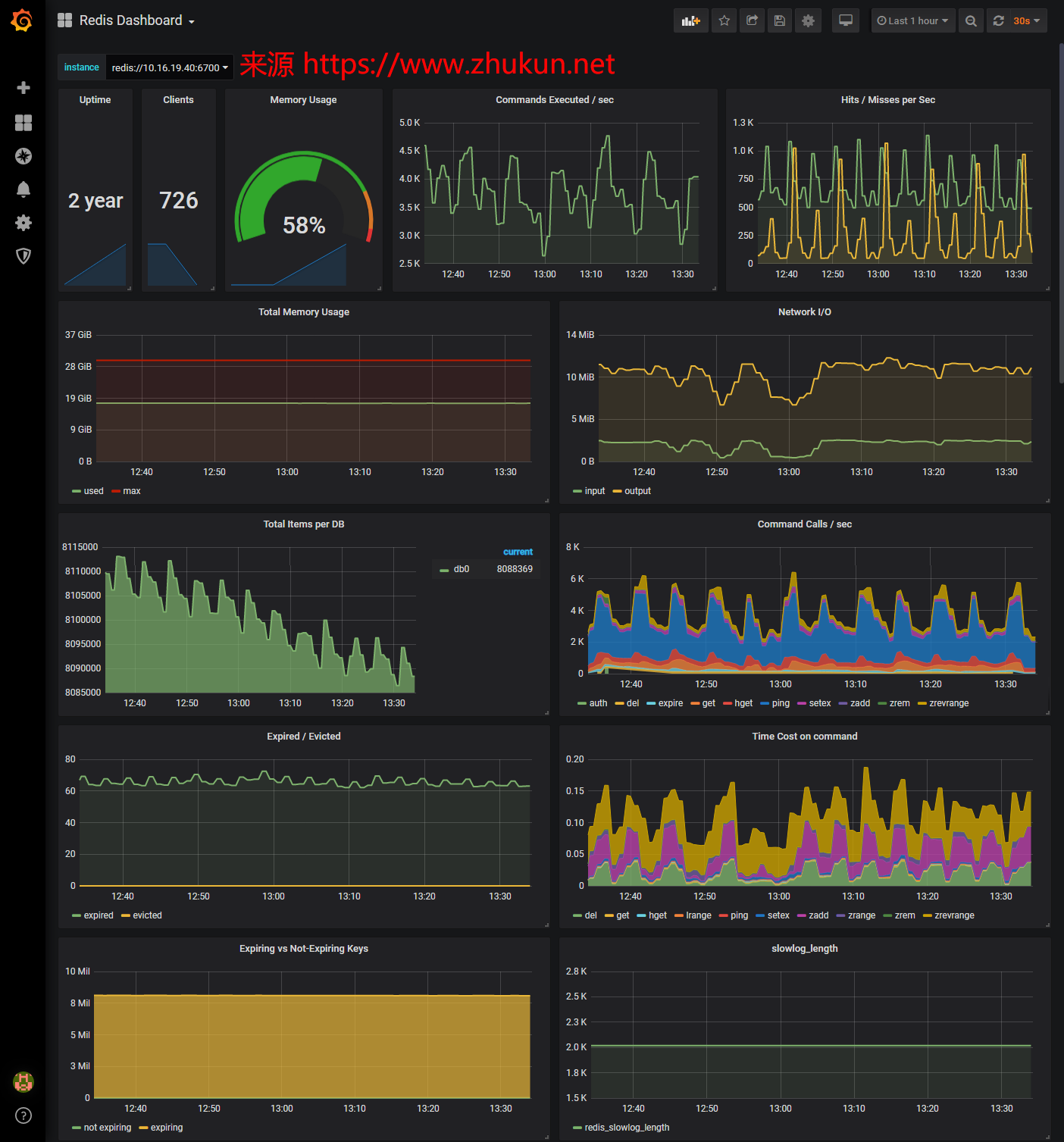
1, 调用Elasticsearch API查询数据
下面的命令是一条标准的查询语句
curl -XGET http://127.0.0.1:9200/my_index-*/_search -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"size": 10000,
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": [
{ "match_all": {} },
{ "match_phrase": { "id": 20202162488675 } },
{ "match_phrase": { "my_site": "www.zhukun.net" } },
{ "match_phrase": { "log_level": "error" } },
{ "range": { "@timestamp": { "gte": "2022-06-09T00:00:00.000+08:00", "lte": "2022-06-09T23:59:59.999+08:00" } } }
]
}
}
}'2, 将查询到的数据导出为csv格式
首先, 我们将上面的命令查询的结果重定向到a.json文件中, 然后使用jq命令将json中的数据导出为csv
jq '[ .hits.hits[]._source ] | map(del(.message)) | (map(keys) | add | unique) as $cols | map(. as $row | $cols | map($row[.])) as $rows | $cols, $rows[] | @csv' a.json > a.csv3, 一些注意事项
3.1 查询命令里的”size”: 10000表示查询结果的最大显示数量, 受到ES的index.max_result_window的限制(默认限制是10000条), 如果要修改此限制可使用如下命令:
curl -XPUT http://127.0.0.1:9200/my_index-*/_settings -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"index": { "max_result_window": 50000 }
}'3.2 关于jq命令的用法
- [ .hits.hits[]._source ]表示将所有结果放在一个list里
- map(del(.message))表示删除结果里的message这个k-v
- map(keys) | add | unique表示提取所有的key