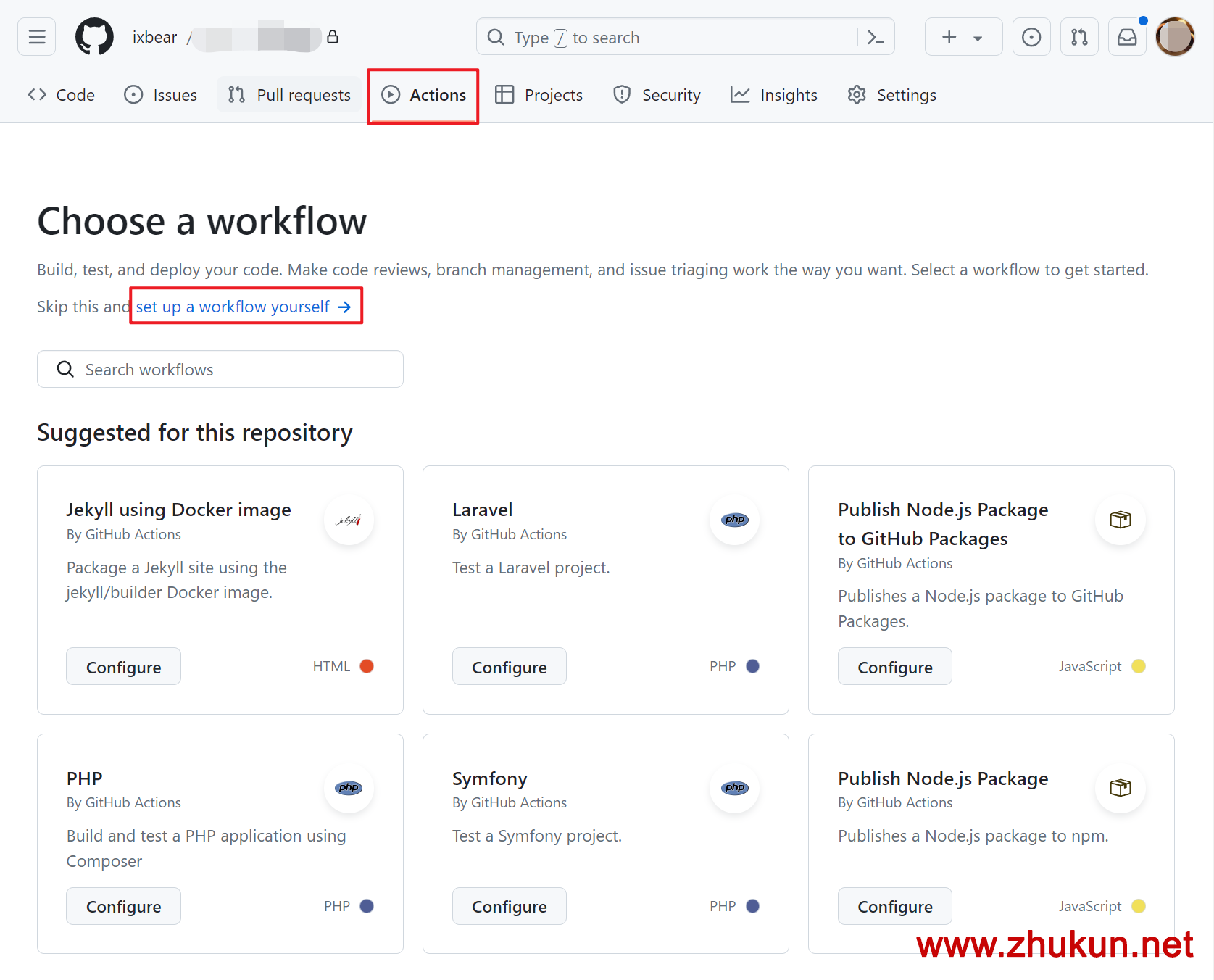
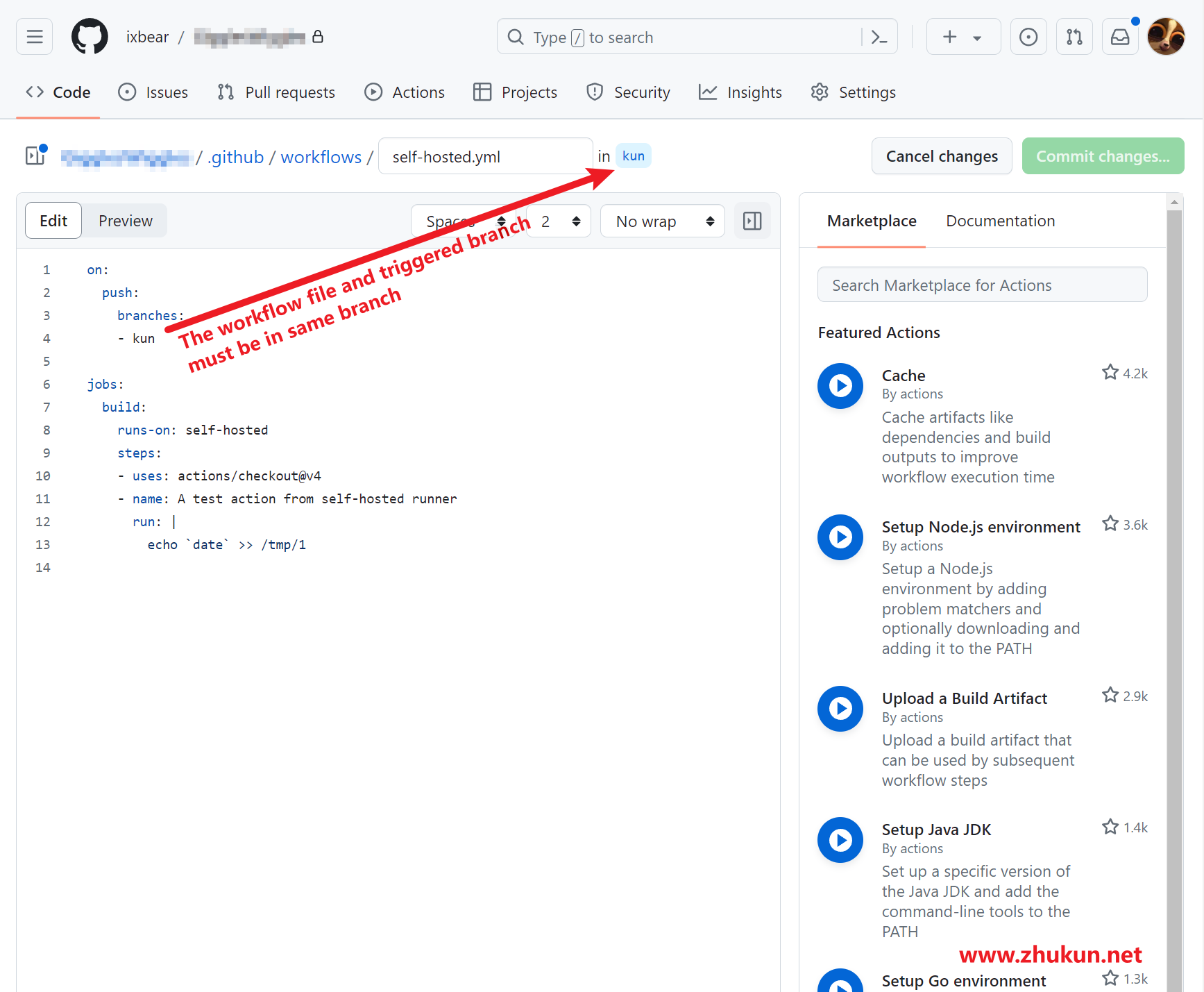
Set up self-hosted runners for Github Actions
Add and Install a new runner on our host
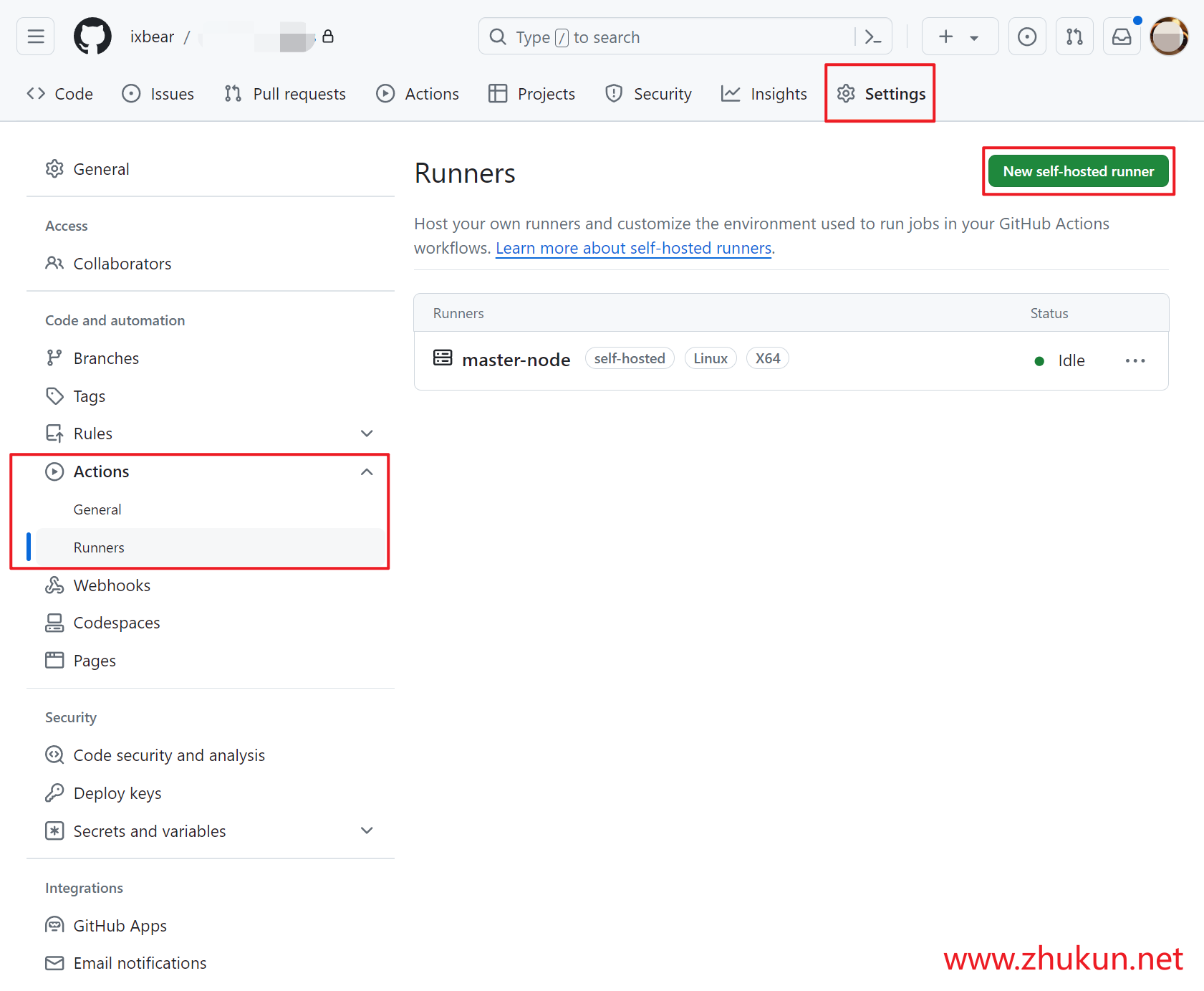
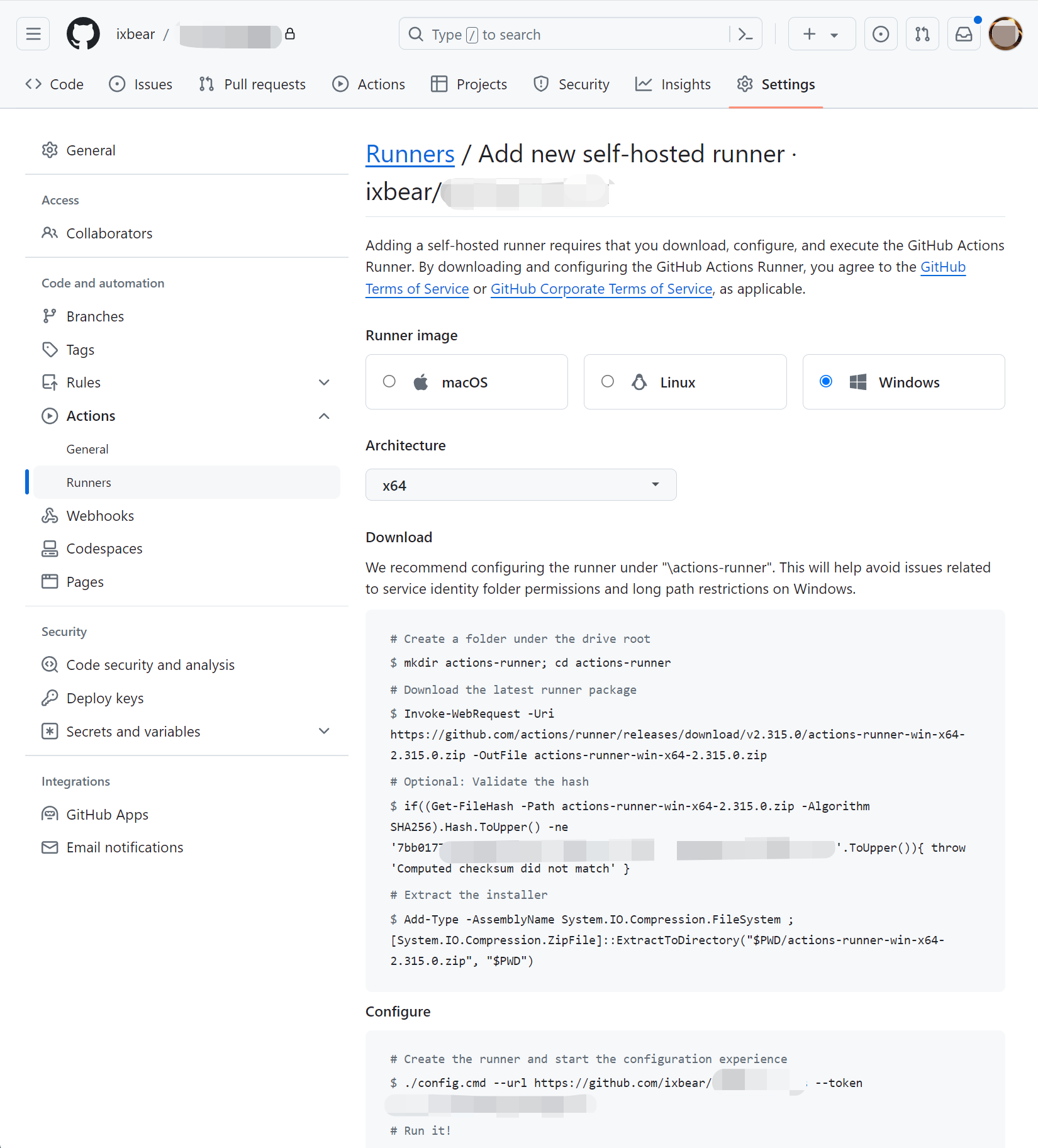
Highly recommand run self-hosted runner as a systemd service
# Save settings
./config.cmd --url https://github.com/XXX/MyApp --token XXXXXXXXX
# Lets's deploy a systemd service
# Refer: https://docs.github.com/en/actions/hosting-your-own-runners/managing-self-hosted-runners/configuring-the-self-hosted-runner-application-as-a-service
sudo ./svc.sh installThen, we will see these below
Run as user: zhang3
Run as uid: 1000
gid: 1000
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/actions.runner.XXX.service → /etc/systemd/system/actions.runner.XXX.service.Set up the workflow for our Github Actions