内网穿透: 使用ssh tunnel将内网主机映射到公网
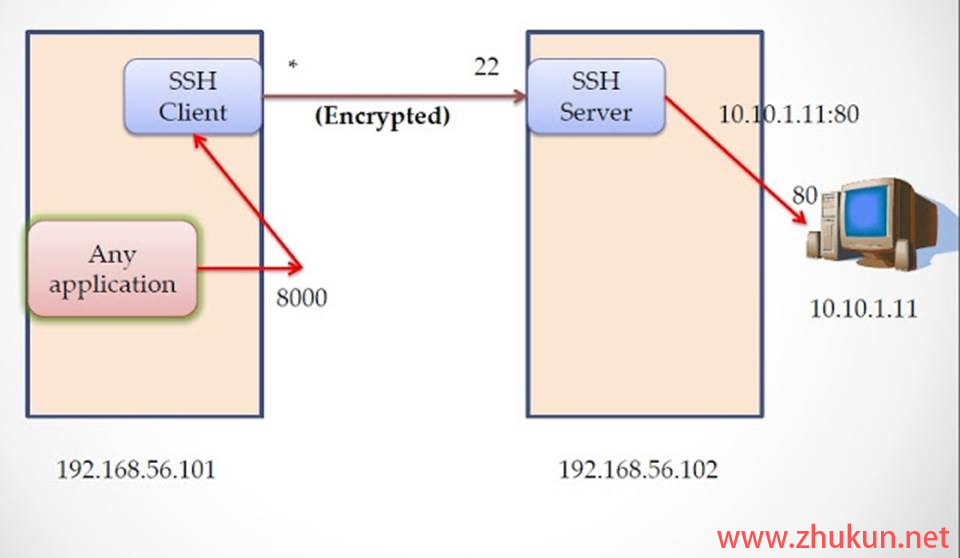
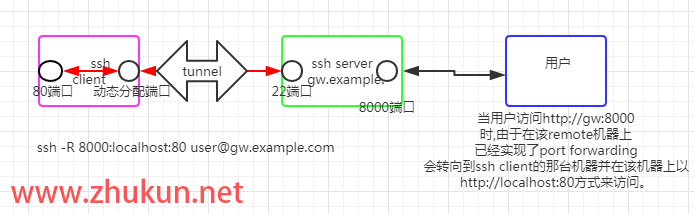
如果希望将一台内网中的主机发布到公网(使用阿里云/腾讯云中转的方式), 使得该内网主机可以在全球任意地点被访问, 仅需要用到ssh即可. 用到的原理就是ssh的remote port forwarding特性, 具体可参考本博客之前写的简单解释 ssh 中的 local port forwarding 和 remote port forwarding.
假设我们已经有了一台阿里云/腾讯云的主机, 其公网IP是1.1.1.1, 需要在ssh配置里启用GatewayPorts(否则ssh tunnel建立以后只会监听127.0.0.1)
在我们的内网主机上写入一个systemd服务
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/[email protected] # 写入如下内容
[Unit]
Description=Persistent SSH Tunnel to from port 127.0.0.1:%i on this server to port 3389 on external server(1.1.1.1:3389)
After=network.target
[Service]
Environment="LOCAL_PORT=%i"
ExecStart=/usr/bin/ssh -NTC -o ServerAliveInterval=60 -o ExitOnForwardFailure=yes -R 3389:0.0.0.0:${LOCAL_PORT} [email protected]
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
参数解释:
T: 禁止分配伪终端
N: 不执行远程指令
C: 请求压缩所有数据
然后启用服务
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable ssh-tunnel@22 --now然后就可以通过1.1.1.1:3389来访问这台内网主机的22端口了.
参考文档: README-setup-tunnel-as-systemd-service.md
Read More